According to many experts, chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory disease caused by infection with the eventual addition of autoimmune disorders, characterized by damage to the parenchymal and interstitial tissue of the organ.The disease has been known to medicine since 1850, but even today it remains poorly understood and difficult to treat.Chronic bacterial (6 - 10%) and non -bacterial (80 - 90%) prostatitis are the most common and socially significant inflammatory diseases in men, which significantly reduces their quality of life.The disease is mainly reported in young and middle -aged people and is often complicated by disorders of copulative and generative functions (reduced potency, infertility, etc.).The disease is reported in men in 8 - 35% of cases aged 20 to 40 years.
The cause of bacterial prostatitis is a pyogenic flora, which penetrates the gland from the urethra or the lymphogenic and hematogenous pathways.The etiology of chronic non -bacterial prostatitis and its pathogenesis remain unknown.It mainly affects men over 50.
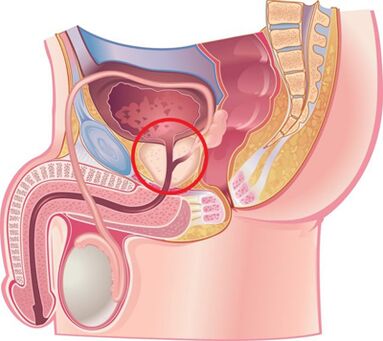
Causes for the development of the disease
Currently, chronic prostatitis is considered a polyethological disease.There is an opinion that the disease occurs as a result of an infection entering the prostate, and then the pathological process takes place without its participation.This is facilitated by a number of non -infectious factors.
Infectious factors for the development of chronic prostatitis
In 90% of cases, pathogens enter the gland from the urethra, leading to acute or chronic prostatitis.There are cases of asymptomatic transport.The course of the disease is influenced by the state of the defenses of the human body and the biological properties of the pathogen.The transition from acute to chronic prostatitis is thought to occur due to the loss of tissue elasticity due to excess production of fibrous tissue.
The following pathogens have been found among the causes of chronic prostatitis:
- In 90% of cases, the disease reveals gram -negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli), Enterococcus faecalis (Fecal Enterococcus) and a little more often -Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Klebsiella sp.Gram-positive bacteria enterorococci, streptococci and staphylococci are rare.
- The role of coagulase-negative staphylococci, ureaplasm, chlamydia, trichomonas, gardnella, anaerobic bacteria and Candida fungi has not been fully understood.
The infection enters the prostate in several ways:
- The ascending road is the most common, as proven by the common combination of prostatitis and urethritis.
- Hematogenous prostatitis develops when the infection penetrates the gland through the blood, which is observed in chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, periodontitis, pneumonia, cholecystitis and cholangitis, purulent skin diseases, etc.
- In contact, chronic prostatitis develops with urethritis and strictures of the urethra as the infection penetrates the gland, climbing with urine current, with purulent infections of the kidneys, channels of epipidics, protective and fuelitis, during diagnostics, and therapeutic urea.
- Lymphogenic infection penetrates the prostate with procrays, thrombophlebitis of hemorrhoid veins, etc.
Non -infectious factors for the development of chronic prostatitis
Chemical factors
According to experts, the leading role in the development of chronic prostatitis belongs to the intraprostatic reflux urine when urine differs from the urethra to the iron, which leads to impaired emptying of the prostate and seminal vesicles.
With disease vascular reactions develop to the swelling of the organ, nervous and humoral regulation of the tissue of the tissues of the smooth muscle of the urethra and the activation of the alpha are disturbed1-DoDRAceptors cause the development of dynamic obstruction and contribute to the development of new intraprostatic refuxes.
Urants contained in the urine with reflux lead to the development of a "chemical inflammatory response".
Hemodynamic disorders
Support chronic inflammation of blood disorders in the pelvic organs and scrotum.Stagnation develops in persons leading to a sedentary lifestyle, such as drivers, office employees, etc., with obesity, sexual withdrawal, sexual sexual dysmetry, frequent hypothermia, mental and physical overload.Maintaining the inflammatory process, taking spicy and spicy foods, alcohol and smoking, etc.
Other factors
There are many other factors that support the chronic inflammatory process in the prostate.These include:
- Hormonal.
- Biochemical.
- Immune response disorders.
- Autoimmune mechanisms.
- Infectious and allergic processes.
- Characteristics of the structure of the prostate glands, which leads to the difficulty of complete drainage.
Quite often it is not possible to determine the causes of chronic prostatitis.
Prostatitis
According to the classification offered in 1995 by the National Institute of Health of the United States, prostatitis is divided into:
- Sharp (category I).Is 5 - 10%.
- Chronic bacterial (category II).Is 6 - 10%.
- Chronic no -bacterial inflammatory (category IIIA).Is 80 - 90%.
- Chronic non -bacterial non -inflammatory (category IIIB) or chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
- Chronic prostatitis discovered by accident (category IV).
Signs and symptoms of chronic prostatitis
The course of chronic prostatitis is long but not monotonous.Exacerbation periods are replaced by periods of relative lull, which occur after complete anti -inflammatory and antibacterial therapy.
The development of chronic bacterial prostatitis is often preceded by urethritis of bacterial or gonorrhea nature, non -bacterial - blood disorders in the pelvic organs and scrotum (hemorrhoids, varicles, etc.), sexual transitions.
Patients with chronic prostatitis present many complaints.They have been treating doctors for years, but very rarely studied for prostate disease.About a quarter of patients do not complain or the disease continues with scarce clinical symptoms.
Complaints of patients with chronic prostatitis can be conditionally divided into several groups.
Urination disorders associated with narrowing of the urethra:
- Difficulties at the beginning of urination.
- Weak urine stream.
- The flowing or urinated missed.
- Feeling incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Symptoms caused by nerve endings:
- Frequent urination.
- Urination calls are sharp and strong.
- Urination in small portions.
- Urine incontinence during the desire for urination.
Pain Syndrome:
- The intensity and nature of pain vary.
- Pain localization: lower abdomen, perineum, rectum, groin and lower back, inner thighs.
Sexual dysfunction:
- Pain in the rectum and urethra during ejaculation.
- A small erection.
- Loss of orgasm.
- Premature ejaculation, etc.
From the nervous system: neurotic disorders in the form of fixing patients' attention on the condition of their health.
Signs and symptoms of chronic non -bacterial prostatitis
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men (CPP) occurs with the usual symptoms of chronic prostatitis, but there are no bacteria in the 3rd urine and prostate secretions.Chronic non -bacterial interstitial cystitis, diseases of the rectum, spastic myalgia of pelvic floor syndrome and prostate lesions with functional nature caused by disorders of the innervation of the organ and its hemodynamics can simulate CPP.
If the function of neurovegetative is impaired, atony and impaired innervation of the gland are observed, which is manifested by difficulty in the rapid and complete closure of the lumen of the urethra.In this case, after urination, the urine continues to be released with a drop for a long time.In such patients, the study reveals instability and increased excitability, which is manifested by increased sweating and excitability of cardiac activity, changes in dermography.
Complications of the disease
The long course of chronic prostatitis is complicated by disorders of sexual and reproductive functions, the development of diseases such as vesiculitis and epipidimitis, and sclerosis of the organ.Organ sclerosis impairs local microcirculation and urodynamics, as well as the results of surgical interventions.Fibrosis of the perihumetthral tissues leads to the development of urinary disorders.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that there are many reasons for the development of chronic prostatitis, a whole complex of diagnostic tests is used to diagnose it.The success of treatment depends on the proper determination of the causes of the disease.The diagnosis of chronic prostatitis is based on the following data:
- Classic triad of symptoms.
- A complex of physical methods (rectal prostate finger examination).
- A complex of laboratory methods (urine analysis and microscopy of the prostate, sowing and determination of the sensitivity of the microflora to antibacterial drugs, general analysis of urine and blood).
- To detect gonococci, bacterioscopy is smeared with urethra, PCR and serological methods (for the detection of ureaplasms and chlamydia).
- Uroofluometry.
- Prostate biopsy.
- Complex of instrumental methods (ultrasound).
- Determination of the patient's immune status.
- Determination of neurological status.
- If the treatment is ineffective and complications are suspected, computed tomography and magnetic resonance, blood culture, etc. are performed.
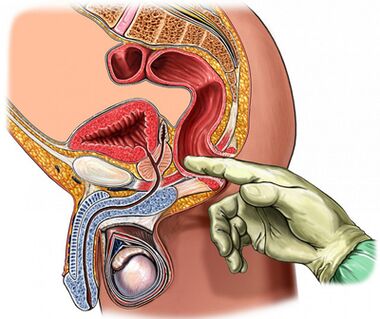
Palpation of the prostate gland
Of paramount importance in the diagnosis of the disease is the palpation of the prostate, which increases during the period of exacerbation and decreases during the period of descent of the inflammatory process.In chronic prostatitis, during the exacerbation period, the gland becomes swollen and painful.
The organ consistency may be different: areas of softening and hardening are palpated and areas of harvest are determined.Through palpation it is possible to evaluate the shape of the gland, the condition of the seminal tubercles and the surrounding tissues.
The process of transverse digital examination is combined with the collection of gland secretions.Sometimes it becomes necessary to obtain the secretion from each forehead individually.
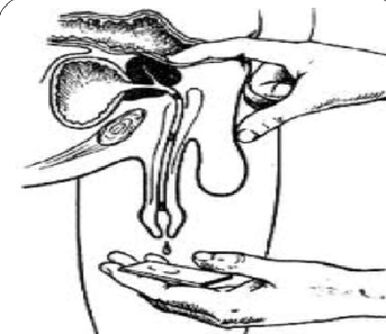
Analysis of a 3-hour urine sample and prostate secretion
The "gold standard" in the diagnosis of chronic prostatitis are:
- Collecting the first part of the urine.
- Collection of the second part of the urine.
- Obtaining gland secretions through massage.
- Collection of the third part of the urine.
A microscopic and bacteriological examination of the material is then performed.
For prostate inflammation:
- The microbial number (CFU) exceeds 103/ml (104/ml for epidermal staphylococci), but the small number of germs, numbering of tens and hundreds should not be neglected.
- The presence of 10-15 leukocytes in the visual area identified by microscopy is a generally accepted criterion for the presence of an inflammatory process.
Prostate secretion and part of the urine are subjected to microscopic and bacteriological examination:
- In chronic bacterial prostatitis, an increase in leukocytes in the secretion of the gland and the third part of the massage part of the urine and bacteria (mainly from the intestinal group) is observed.
- In non -bacterial prostatitis, there is an increase in the number of leukocytes in the secretion of the gland, but the microflora is not detected.
- CPP also does not have an increased number of leukocytes and microflora.
Normal prostate secretion:
- Less than 10 leukocytes per field of view.
- There is a large amount of lecithine grains.
- There is no microflora.
In chronic prostatitis, the following is found in prostate secretion:
- The number of leukocytes is large - exceeding 10-15 in the field of view.
- The number of lecithin grains is reduced.
- The pH of secretion is shifted to the alkaline side.
- The content of acid phosphatase is reduced.
- The activity of lysoosima is increasing.
Obtaining negative results from prostate secretion does not prove the lack of inflammatory process.
The value of the prostate secretion test remains.Usually, during crystallization, a characteristic model is formed in the form of fern leaf.In the event of a violation of the properties of prostatic secretion, such a model does not form, which occurs when the androgen hormonal background changes.
Ultrasound
If prostate disease is suspected, an ultrasound examination of the gland itself (transrectal ultrasound), the kidneys and bladder is optimal, which allows us to determine:
- Volume and size of the gland.
- The presence of stones.
- Dimensions of seminal vesicles.
- Condition of the walls of the bladder.
- Amount of residual urine.
- Scrotum structures.
- Another type of pathology.
Other methods of prostate examination
- The state of urodynamics (urine flow rate) is easily determined and simply determined by study as uroflowmetry.With the help of this study, it is possible to immediately detect signs of obstruction of the bladder output and to do dynamic monitoring.
- A breakthrough biopsy is suspected if abscess, benign hyperplasia and prostate cancer are formed.
- X -ray and endoscopic examination are performed to clarify the causes of the development of infravezicular obstruction.
- In the case of a long -term inflammatory process, it is recommended that urethrocystoscopy be performed.
Differential diagnosis
Chronic Prostatitis Should Be Distinguisted From Vesiculoprostatostostasis, Vegetative Prostatopathy, Congestive Prostatitis, Pelvic Floor SyDystrophy, Inflammatory Diseases of Other Organs: Interstitial Cystitis, Osteitis of the Symphysis Pubis, Sexual Dysfunction, Hypertrophy of the bladder, tumor, tumorUrolithiasis, chronic epipidimitis, inguinal hernia.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
Treatment for chronic prostatitis should begin with changes in the patient's lifestyle and diet.
In the treatment of the disease, medicines are used that affect different parts of the pathogenesis.
Main directions of therapy:
- Elimination of causative microorganisms.
- Anti -inflammatory therapy.
- Normalization of blood circulation in the organs of the prostate and pelvis.
- Normalizing the adequate drainage of prostatic acins.
- Normalize the hormonal profile.
- Prevention of organs.
The following drug groups are used to treat chronic prostatitis:
- Antibacterial.
- Anticholinergic.
- Vasodilators.
- Alpha1- Adrenergic blockers.
- 5 alpha reductase inhibitors.
- Cytokine inhibitors.
- No -high anti -inflammatory anti -inflammatory.
- Angioprotectors.
- Immunomodulators.
- Preparation affecting the exchange of urate.
Antibiotics in the treatment of bacterial chronic prostatitis
Antibacterial therapy should be performed taking into account the sensitivity of detected microorganisms to antibiotics.In the case of pathogen vacant, empirical antimicrobial treatment is used.
Optional medicines are fluoroquinolones of the generation II - IV.They quickly penetrate the tissues of the gland with ordinary methods of use, show activity against a large group of Gram -negative microorganisms, as well as ureaplasma and chlamydia.In case of failure of antimicrobial treatment should be taken:
- Microflora Polyurezancy,
- Short (less than 4 weeks) treatment courses,
- Incorrect selection of antibiotic and its dose,
- changes in the type of pathogen,
- The presence of bacteria that live in the prostate channels covered with a protective extracellular membrane.
The duration of treatment should be at least 4 weeks with the mandatory subsequent bacteriological control.In case of preservation in the 3rd part of the urine and the secret of the prostate bacteriuria more than 103Correspondence is prescribed for R -Antibacterial therapy for a period of 2 to 4 weeks.
Cytokine inhibitors in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
Cytokines are glycoproteins, which are secreted by immune and other cells in conditions of inflammatory reaction and immune response.They are actively involved in the development of a chronic inflammatory process.
Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs
Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs have an anti -inflammatory effect, reduce pain and fever.They are widely used in the treatment of chronic prostatitis in the form of tablets and suppositories.The most effective is the rectal route of introduction.
Immunotherapy
Immunomodulatory agents are used in the treatment of bacterial chronic prostatitis, in addition to antibiotics and antibiotic drugs.The most effective is the rectal path of their introduction.The immunomodulator is widely used, which increases the functional activity of phagocytes, which contributes to more effective elimination of pathogens.
Alpha-blockers in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
Alpha-1 adrenergic shoes have been found to normalize the tone of the smooth muscles of the prostatic part of the urethra, seminal bubbles and prostate capsules, which makes medicines in this group very effective in treating the disease.Alpha-1 adrenergic shoes are used in patients with pronounced urinary disorders in the absence of an active inflammatory process.
In CTB, the treatment period is from 1 to 6 months.
5a reductase inhibitor in the treatment of abacus prostatitis and KTBB
With the influence of the 5A reductase enzyme testosterone, the 5A-dichidotrotestosterone is converted to a prostatic form, the activity of which in the prostate cells is more than 5 times higher than the activity of the testosterone itself, which in the elderly leads to an increase in the organ due to epithelial and stromal components.
When taking an inhibitor of 5A reductase for 3 months, atrophy of the stromal tissue is observed, for 6 months-evil the secretory function is inhibited, the severity of the pain and the volume of the gland is reduced, the tension and the edema of the organ decrease.
The role of anti -triggered drugs in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
With a long inflammation in the prostate gland, fibrosis develops, which is manifested by disorders of microcirculation and urodynamics.Anti -processing drugs are used to prevent the fibrification process.
Other medicines used in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
Along with the above medicines, the disease is used to treat the disease:
- Antihistamines.
- Vasodilators and angioprotectors.
- Immunosuppressants.
- Preparations that affect the exchange of urates and trinodium salt of citric acid.
Vegetable
Effective in the treatment of prostatitis, the use of the drug in the form of candles containing a complex of biologically active peptides isolated from the prostate gland of cattle.
Under the influence of the drug,:
- Stimulating metabolic processes in the tissues of the gland.
- Improve microcirculation.
- Reduction of edema, leukocyte infiltration, stagnation and pain.
- Prevention of thrombosis in the prostate gland venles.
- Increasing the activity of Acinus secretory epithelium.
- Improve sexual function (increased libido, restore erectile function and normalize spermatogenesis).
Finger massage of prostate gland
A number of researchers say that chronic prostatitis should be used finger massage, taking into account known contraindications.
Physiotherapy
The effectiveness of physiotherapy procedures in the treatment of prostatitis has not been proven today, the mechanism of action has not been scientifically established, no side effects have been studied.
Prevention of chronic prostatitis
Starting the prevention of the development of chronic prostatitis, you should know:
- The risk of developing the disease has increased over the years.
- Representatives of the Negro race are more proposed to the disease.
- The family predisposition to the disease is not excluded.
People with a predisposition to the development of chronic prostatitis should be more careful to their health.
Disease Prevention Tips:
- Take a sufficient amount of liquid.Frequent urination promotes the urethral microflora leakage.
- Prevention of diarrhea and constipation.
- Stick to a rational diet.Do not eat food saturated with carbohydrates and saturated fats, leading to weight gain.
- It should be limited to the use of substances that irritate the urethra: spicy and spicy dishes, smoked meats, sauces and spices, coffee and alcohol.
- Refuse smoking.Nicotine adversely affects the condition of the vascular walls.
- Do not overfill.
- Do not hold the bladder emptying.
- Have an active lifestyle, play sports.Do the exercises to strengthen the muscles of the pelvis, allowing you to remove the stagnation of venous blood, which in turn maintains the normal function of the prostate gland.
- Have a regular sex life.Avoid prolonged abstinence.Iron must be released in a timely manner from the secret.
- Stay supporters of monogamous relationships.Illegal sexual relations increase the likelihood of acquiring sexually transmitted diseases.
- If the complaints appear from the genius, contact a urologist immediately.